Understanding different types of inhalers
Choosing or switching your inhaler should be a shared decision between you and your clinician. Matching an inhaler to your own ability and preference can improve both technique and your health. Make sure you follow the instructions for your inhaler provided by your chemist or clinician. Different inhalers can use different techniques.
Dry Powder Inhalers (DPIs) – these give your medicine in the form of a dry powder instead of a spray. These require patients to inhaler quickly and deeply.
Pressurised metered dose inhalers (pMDIs) – provide medicine in a spray form (aerosol), you must use these with a spacer. Patients are required to inhaler slow and steady.
Soft Mist Inhalers (SMIs) – These change liquid medicine into a mist that can be inhaled. SMIs are thought to deposit less medication on the back of the throat, meaning that more of it reaches the lungs. Patients should inhaler slow and steady.
Why you should use a Spacer with an inhaler
Using a spacer with your Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI) is a more effective way of getting medication to your lungs.
It also helps to prevent deposits of inhaled medication in your mouth and stomach.
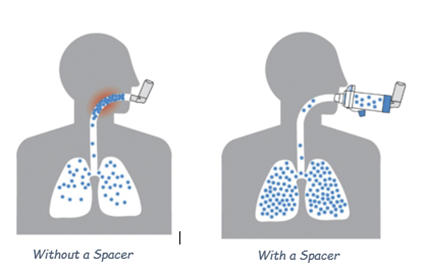
(Image from Mcivor, Devlin, and Kaplin, 2018)
Seven Steps to Good Inhaler Technique
- Prepare the inhaler device by removing the cap. If using a Metered Dose inhaler please shake well too.
- Prepare OR load the dose as instructed (use a spacer if a Metered Dose Inhaler).
- Breathe out, fully and gently, but not into the inhaler.
- Place mouthpiece in your mouth and seal your lips around the mouthpiece.
- Breathe in. Different inhalers use different techniques. Follow the instructions provided by your clinician, nurse or Pharmacist.
- Pressurised Metered Inhaler: Slow and Steady
- Soft Mist Inhaler: Slow and Steady
- Dry Powder Inhaler DPI: Quick and Deep
- Remove inhaler from the mouth and hold the breath for up to 10 seconds.
- Wait for a few seconds then repeat as necessary.
Carbon footprint and your inhaler
Did you know you may be able to use an environmentally friendly inhaler? It is important to use the right inhaler for your needs but some of these are better for our planet.
Did you know?
- A Dry Powder Inhaler use around 7g of co2e per actuation (1 press).
- A Metered Dose Inhaler use around 100g of co2e per actuation (1 press).
1000 inhalers emit the equivalent of
- 12.1 Tonnes of Greenhouse gases.
- 46,370 diesel road miles.
- Would need 459 trees to absorb emissions.
Ask your clinician today about a greener option?
Further information about using your inhaler
- Respiratory Care at George Eliot Hospital
- Patient Information Leaflets
- Respiratory Support patient group
- Singing for Breathing patient group
- Asthma and Lung UK
George Eliot Hospital is a smoke free environment. For help and advice to stop smoking you can call the national helpline on 0300 123 1044 or visit https://
Copyright
Figure of an inhaler being used with and without a spacer taken from Mcivor, RA., Devlin, H.M. and Kaplin, A. (2018) 'Optimising the Delivery of Inhaled Medication for Respiratory Patients: The Role of Valved Holding Chambers', Canadian Respiratory Journal, Article ID 5076259. Available at: https://
George Eliot Hospital. (2024). How do I use a Metered Dose inhaler? [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7m89Pn-OVLI. Copyright of George Eliot Hospital.
George Eliot Hospital. (2024). How do I use a Dry Powder inhaler? [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9HUplpiKykE Copyright of George Eliot Hospital.
Except where otherwise noted, this item is licensed under the CC BY license (https://
If you are a rights holder and are concerned that you have found material on our patient information resources website, for which you have not given permission, or is not covered by a limitation or exception in national law, please contact us using the Feedback form providing your contact information and full details of the material.

